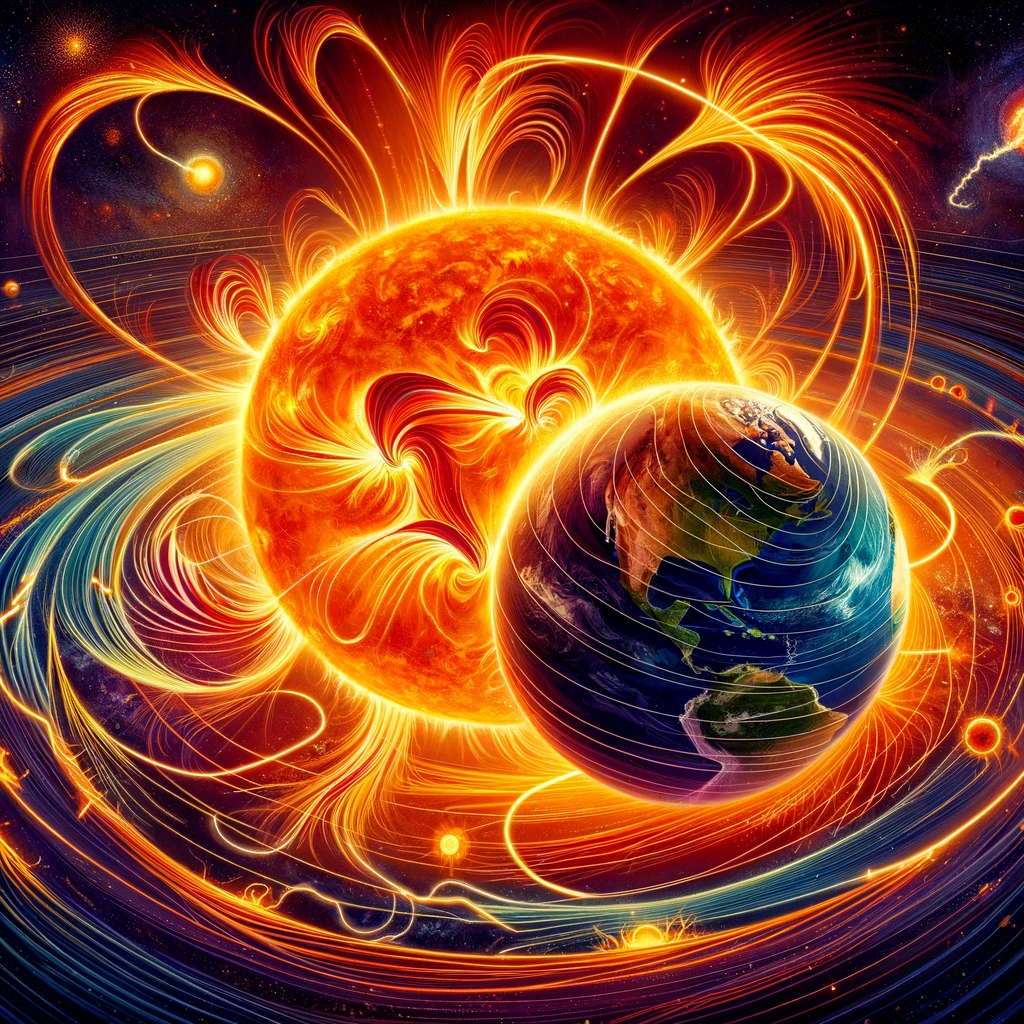
The Sun, the life-giving star at the center of our solar system, undergoes a fascinating yet poorly understood phenomenon: the reversal of its magnetic poles. Occurring approximately every 11 years, this event is part of the larger solar cycle, which influences space weather and, consequently, life on Earth. But what does this mean for us? Should we be concerned about these changes? This article delves into the science behind the Sun’s magnetic pole reversal, explores what the scientific community has to say, and examines the implications for our planet.
Understanding the Sun’s Magnetic Cycle
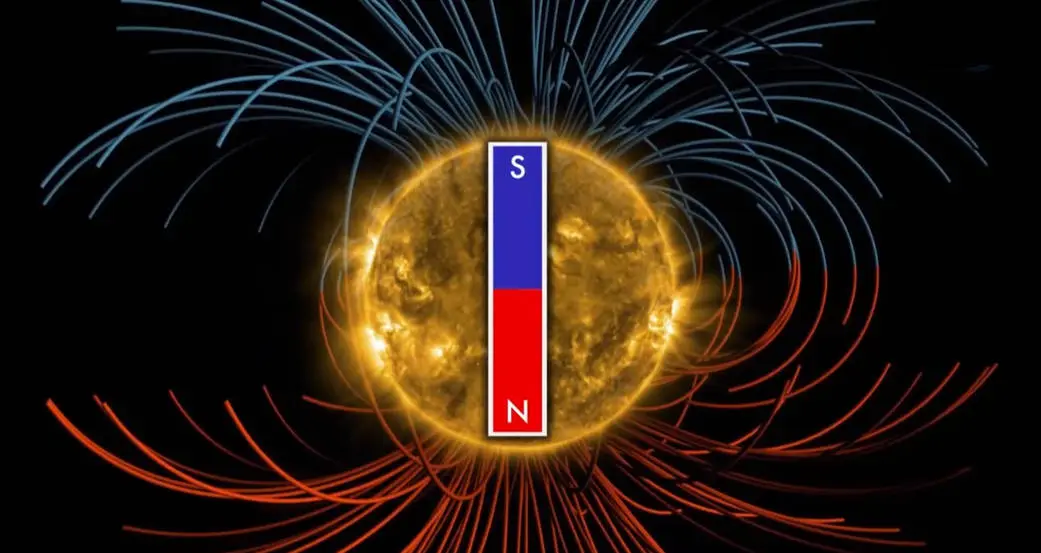
The solar cycle plays a crucial role in the dynamics of the Sun’s magnetic field. Every 11 years, the Sun’s magnetic poles switch places, a process intertwined with the cycle of solar activity, including sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections. Understanding this cycle is not only fascinating from a scientific standpoint but also crucial for predicting space weather that can affect satellite operations, communication systems, and even power grids on Earth.
The Science Behind Magnetic Pole Reversal
At the heart of the solar magnetic pole reversal is the solar dynamo, a complex mechanism that generates the Sun’s magnetic field. This section explains the processes that lead to the flipping of the magnetic poles, offering insights into the phenomena that drive solar activity and its cyclic nature.
Current Research and Discoveries
Thanks to advanced observatories and space missions, scientists have made significant progress in understanding the Sun’s magnetic activities. Recent discoveries have shed light on the intricate patterns of solar magnetic fields and their evolution, providing valuable data to refine our predictions of solar phenomena.
Implications for Earth and Its Inhabitants
The most significant effect of the Sun’s magnetic pole reversal on Earth is an increase in geomagnetic storms. These storms, caused by solar wind interacting with Earth’s magnetosphere, can lead to the awe-inspiring display of the auroras near the polar regions. While these natural light shows are a treat for observers, intense geomagnetic storms have the potential to disrupt satellite communications, navigation systems, and even power grids on a large scale.

Should We Be Worried?
Amid the scientific exploration of the Sun’s magnetic pole reversal, a critical question arises: should humanity be concerned? While sensational headlines might paint a doomsday scenario, the scientific consensus tells a different story. Experts agree that while solar activity can indeed affect Earth in various ways, including disrupting communication networks and power grids, the phenomenon is a natural part of our star’s life cycle and not a harbinger of catastrophe. Mitigation strategies, such as strengthening our technological infrastructure and improving early warning systems, are in place to minimize potential impacts.
Debunking Myths and Misconceptions
Misinformation often surrounds the topic of the Sun’s magnetic pole reversal, leading to unnecessary alarm. It’s crucial to understand that this event will not lead to dramatic shifts in Earth’s climate or geography. The Sun has undergone numerous pole reversals throughout history without catastrophic consequences for life on Earth. This section aims to clarify these misconceptions, reassuring the public with facts grounded in scientific research.
How Scientists Monitor and Predict Solar Activity
The monitoring and prediction of solar activity have advanced significantly in recent years. Observatories on Earth and in space, such as the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and the Parker Solar Probe, play pivotal roles in observing the Sun’s magnetic field and solar phenomena. Additionally, advancements in AI and machine learning have enhanced our ability to predict solar cycles and their potential impacts on Earth, aiding in the development of more effective preparedness strategies.
The Importance of International Collaboration in Solar Research
Understanding and preparing for the effects of solar activity requires a global effort. International collaboration among space agencies, such as NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), and ROSCOSMOS (Russian Space Agency), alongside numerous research institutions, has been crucial in advancing our knowledge of the Sun and its influence on the solar system. These partnerships facilitate the sharing of data, resources, and insights, accelerating scientific discoveries and technological innovations.
What History Tells Us About Solar Activity
Historical records of solar activity, including observations of sunspots and auroras dating back centuries, provide valuable insights into the Sun’s behavior over time. Studies of ice cores and tree rings have also contributed to our understanding of past solar cycles and their impacts on Earth’s climate. These historical perspectives underline the cyclic nature of solar activity and its long-standing influence on our planet.
The Role of the Sun in Our Solar System’s Dynamics
The Sun’s magnetic activity does not only affect Earth but also has implications for the entire solar system. Variations in solar wind can alter the environments of other planets and the heliosphere—the vast bubble of magnetic fields and charged particles that surrounds the solar system. Understanding the Sun’s magnetic cycle is therefore essential for comprehending the broader dynamics of our solar neighborhood.
Preparing for the Future: Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
As our understanding of the Sun’s magnetic cycles and their implications for Earth improves, so does our ability to prepare for and mitigate potential impacts. Governments, space agencies, and international organizations are developing strategies to protect critical infrastructure, such as power grids and communication networks, from the effects of severe space weather. Public awareness and education on these topics are also increasing, empowering individuals and communities to understand and respond to solar-related phenomena.
Engaging with the Scientific Community
Engagement with the scientific community can also enhance one’s understanding of the Sun’s magnetic pole reversal. Participating in public lectures, science fairs, and online forums can provide opportunities to learn from experts and ask questions directly. Many universities and research institutions host public events that cover space science topics, including solar phenomena.
Visual Aids and Interactive Experiences
To complement this article, visual aids such as infographics, diagrams, and animations can help illustrate the complex processes behind the Sun’s magnetic pole reversal and its effects on the solar system. Interactive experiences, such as virtual reality (VR) tours of the Sun and augmented reality (AR) apps that simulate solar activity, can also provide immersive ways to explore this topic.
Understanding the Sun’s magnetic pole reversal is crucial for comprehending the broader dynamics of our solar system and the ways in which solar activity impacts Earth. Through continued research, international collaboration, and public education, we can demystify this phenomenon and better prepare for its effects. As we advance our knowledge and technologies, humanity’s resilience in the face of solar changes continues to strengthen, ensuring that we can navigate future solar cycles with confidence.
By staying informed and engaging with the wealth of available resources, everyone can play a part in unraveling the mysteries of our Sun and safeguarding our planet against the challenges posed by space weather.
Sam Estes
Teagan Piñeda
Outstanding feature
Insightful piece
delectus consequatur sint rerum non illo reiciendis sint illum illum voluptates inventore quisquam deserunt. cupiditate sit vel illum repellendus dolores rem eligendi necessitatibus impedit totam fugit odio. illum iste aut odio illo enim magnam dolor atque nam et. facilis repellat minima non impedit excepturi sapiente ut quaerat repellendus excepturi dicta repellendus rerum pariatur eum harum velit incidunt qui.